Neural ALU Implemented in x86 Assembly
The recent Deepmind’s Neural Arithmetic Logic Unit(NALU) is a very neat idea. It is a simple module that enables numeracy for neural nets. Contrary to popular belief, neural nets are not very good at arithmetic and counting(if at all). If you train an adder network between 0 and 10, it will do okay if you give it 3 + 5 but won’t be able to extrapolate and will fail miserably for 1000 + 3000. Similarly, if the net is trained to count up to 10, it won’t be able to count to 20. The NALU is able to track time, perform arithmetic, translate numerical language into scalars, execute computer code, and count objects in images.
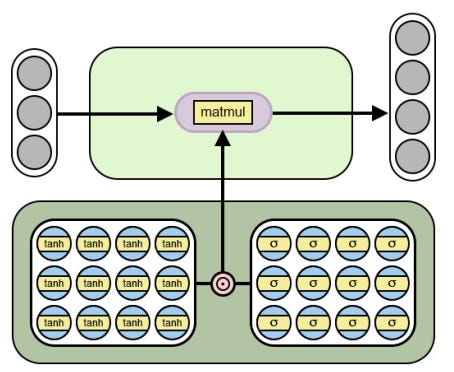
The central idea behind Neural ALU is a differentiable function that outputs 0, -1 or 1, rendering the concept of addition and subtraction trainable. The beauty also lies in the simplicity of the formula: tanh(m) * sigmoid(w) made of fundamental building blocks. If you think about it: tanh is -1 or 1, sigmoid is 0 or 1 so the product of two would be one of 0, 1, -1.
Here is the plot of the function:

This image shows what the NAC looks like:
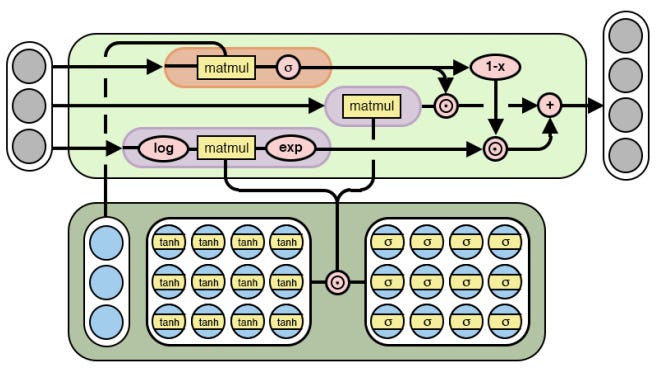
NALU is just NAC cast into log space and back with a learned gate:
The cost function is
0.5 * (y_hat - y) ** 2
so the partial derivative dJ/dm_0 is
dJ/dm_0 = (y_hat - y) * dy_hat/dm_0
= (y_hat - y) * d(x0 * tanh(m_0) * sigmoid(w_0))/dm_0
= (y_hat - y) * x0 * dtanh(m_0) * sigmoid(w_0)
Here is a toy NALU implemented in x86(with SSE!) that uses real Intel FPU ALUs.
; Neural ALU implementation in x86_64
;
; nasm -felf64 nalu.s
; gcc -no-pie nalu.o -o nalu -g
;
%define USE_SUB 1
%define EPOCH 1_000_000
global main
extern printf
section .data
first_fmt: db "first weight: %f, ", 0
second_fmt: db "second weight: %f", 0xA, 0
rand_seed: dd 1
rand_max: dd -2147483648 ; -2^31
section .bss
result: resq 2 ; reserve 2 floats
PRN: resq 2
w_hats: resq 2
m_hats: resq 2
xs: resd 2
tanhs: resd 2
sigms: resd 2
tmp1: resq 2
tmp2: resq 2
weights: resq 1
err: resq 2
section .text
main:
mov ebx, EPOCH
.calc:
cmp ebx, 0
je .exit
dec ebx
.init_rand:
call rand
fstp dword [xs]
call rand
fstp dword [xs+4]
.tanhs_and_sigmoids:
;; first calculate tanhs and put those in tanhs
finit
fld dword [m_hats]
call tanh
fstp dword [tanhs]
finit
fld dword [m_hats+4]
call tanh
fstp dword [tanhs+4]
;; calculate sigmoids
finit
fld dword [w_hats]
call sigmoid
fstp dword [sigms]
finit
fld dword [w_hats+4]
call sigmoid
fstp dword [sigms+4]
.forward_pass:
movdqu xmm0, [tanhs] ; move 128 bits
movdqu xmm1, [sigms]
movq xmm2, [xs] ; move 64 bits
mulps xmm0, xmm1 ; tanh * sigmoid
movdqu [weights], xmm0
mulps xmm0, xmm2 ; tanh * sigmoid * xs
haddps xmm0, xmm0 ; y_hat
haddps xmm0, xmm0 ; horizontal add (sum)
%if USE_SUB
hsubps xmm2, xmm2 ; y = x0 - x1
hsubps xmm2, xmm2
%else
haddps xmm2, xmm2 ; y = x0 + x1
haddps xmm2, xmm2
%endif
.calc_error:
subps xmm0, xmm2 ; xmm0 <- y_hat - y
extractps eax, xmm0, 1
mov [err], eax
.backpropagate:
finit
;; m[0] -= err * x0 * sigm0 * dtanh(m[0]);
fld dword [m_hats] ; dtanh(m0)
call dtanh
fld dword [xs] ; x0
fmul
fld dword [err] ; err
fmul
fld dword [sigms] ; sigm0
fmul
fld dword [m_hats] ; dtanh(m0)
fsubr
fstp dword [m_hats]
finit
;; m[1] -= err * x1 * sigm1 * dtanh(m[1]);
fld dword [m_hats+4] ; dtanh(m1)
call dtanh
fld dword [xs+4] ; x1
fmul
fld dword [err] ; err
fmul
fld dword [sigms+4] ; sigm1
fmul
fld dword [m_hats+4] ; dtanh(m1)
fsubr
fstp dword [m_hats+4]
finit
;; w[0] -= err * x0 * dsigmoid(w[0]) * tanh0;
fld dword [w_hats]
call dsigmoid
fld dword [xs]
fmul
fld dword [err]
fmul
fld dword [tanhs]
fmul
fld dword [w_hats]
fsubr
fstp dword [w_hats]
finit
;; w[1] -= err * x1 * dsigmoid(w[1]) * tanh1;
fld dword [w_hats+4]
call dsigmoid
fld dword [xs+4]
fmul
fld dword [err]
fmul
fld dword [tanhs+4]
fmul
fld dword [w_hats+4]
fsubr
fstp dword [w_hats+4]
.print:
sub rsp, 8 ; reserve stack pointer
movd xmm0, [weights] ; pass result to printf via xmm0
cvtps2pd xmm0, xmm0 ; convert float to double
mov rdi, first_fmt ; printf format string
mov rax, 1 ; number of varargs
call printf ; call printf
add rsp, 8 ; add stack pointer back
sub rsp, 8 ; reserve stack pointer
movd xmm0, [weights+4] ; pass result to printf via xmm0
cvtps2pd xmm0, xmm0 ; convert float to double
mov rdi, second_fmt ; printf format string
mov rax, 1 ; number of varargs
call printf ; call printf
add rsp, 8 ; add stack pointer back
jmp .calc
.exit:
mov eax, 0x60
xor edi, edi
syscall
tanh: ; (exp(x) - exp(-1)) / (exp(x) + exp(-x))
fst dword [tmp1] ; tmp1 <- x
call exp; ; exp(x)
fst dword [tmp2] ; tmp2 <- exp(x)
fld dword [tmp1]
fchs
call exp
fst dword [tmp1] ; tmp1 <- exp(-x)
fld dword [tmp2]
fsubr
fld dword [tmp2] ; load exp(x) and exp(-x)
fld dword [tmp1]
fadd
fdiv
ret
dtanh: ; 1. - pow(tanh(x), 2.)
call tanh
fst dword [tmp1] ; duplicate tanh on the stack
fld dword [tmp1]
fmul ; tanh(x) * tanh(x)
fld1 ; load 1
fsubr ; 1 - tanh(x) ** 2
ret
sigmoid: ; 1 / (1 + exp(-x))
fchs ; -x
call exp ; exp(-x)
fld1 ; load 1
fadd
fld1 ; load 1
fdivr ; 1 / ST(0)
ret
dsigmoid: ; sigmoid(x) * (1. - sigmoid(x))
call sigmoid
fst dword [tmp1] ; tmp <- sigmoid(x)
fchs
fld1
fadd
fld dword [tmp1] ; st(0) <- sigmoid(x)
fmul
ret
exp:
fldl2e
fmulp st1,st0 ; st0 = x*log2(e) = tmp1
fld1
fscale ; st0 = 2^int(tmp1), st1=tmp1
fxch
fld1
fxch ; st0 = tmp1, st1=1, st2=2^int(tmp1)
fprem ; st0 = fract(tmp1) = tmp2
f2xm1 ; st0 = 2^(tmp2) - 1 = tmp3
faddp st1,st0 ; st0 = tmp3+1, st1 = 2^int(tmp1)
fmulp st1,st0 ; st0 = 2^int(tmp1) + 2^fract(tmp1) = 2^(x*log2(e))
ret
rand:
imul eax, dword [rand_seed], 16807 ; RandSeed *= 16807
mov dword [rand_seed], eax
fild dword [rand_seed] ; load RandSeed as an integer
fidiv dword [rand_max] ; div by max int value (absolute) = eax / (-2^31)
ret
If you run this, the first tanh * sigmoid goes to 1 and second one go to -1.
Epoch l0 l1
0 0.0 0.0
50000 0.987506901824 -0.987548950867
100000 0.991264033674 -0.991189817923
150000 0.992845113954 -0.992861588357
200000 0.993821244128 -0.993813140853
250000 0.994479531604 -0.994470005826
300000 0.994956870738 -0.994965214447
350000 0.995335580972 -0.995335751094
400000 0.995641550629 -0.995639510579
450000 0.99588903762 -0.995888041575
500000 0.996102719885 -0.996098271471
550000 0.996282859485 -0.996286010814
600000 0.996444518075 -0.996441767134
650000 0.996583070776 -0.996582158171
700000 0.996711963875 -0.99670336452
750000 0.996820796932 -0.996818826574
800000 0.996921023282 -0.9969240341
850000 0.997012684359 -0.997014549213
900000 0.997100144072 -0.997097107772
950000 0.997177851616 -0.99717492668
Here is a runnable NAC toy example implemented in python:
from random import random
import math
def tanh(x):
return math.tanh(x)
def dtanh(x):
return 1. - math.tanh(x) ** 2
def sigmoid(x):
return 1 / (1 + math.exp(-x))
def dsigmoid(x):
return sigmoid(x)*(1-sigmoid(x))
m0 = m1 = w0 = w1 = 0.0
for i in range(1000000):
x0 = random()
x1 = random()
y = x0 - x1
# forward pass
l0 = tanh(m0) * sigmoid(w0)
l1 = tanh(m1) * sigmoid(w1)
y_h = l0 * x0 + l1 * x1
# calculate error
e = y_h - y
# backpropagation
m0 -= e * x0 * sigmoid(w0) * dtanh(m0)
m1 -= e * x1 * sigmoid(w1) * dtanh(m1)
w0 -= e * x0 * dsigmoid(w0) * tanh(m0)
w1 -= e * x1 * dsigmoid(w1) * tanh(m1)
if not i % 50000:
print i, l0, l1
You should see the neural net converge immediately.
Source
-
Neural Accumulator(NAC) Source: arXiv:1808.00508 [cs.NE]